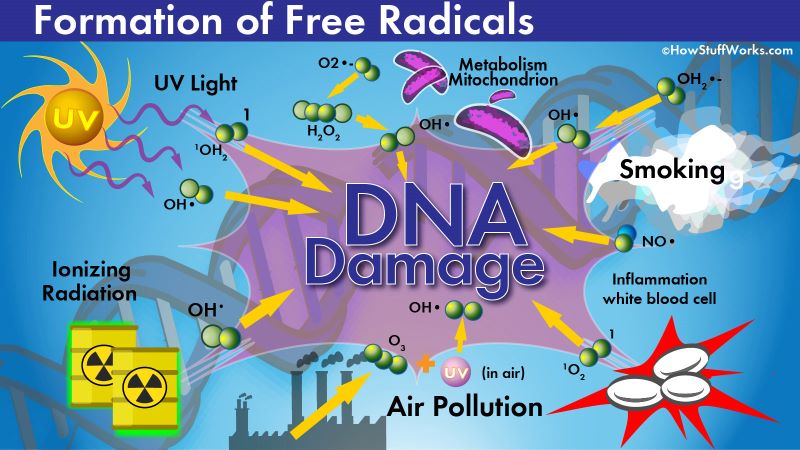
Negative Effects of Free Radicals
- Aging
- Cancer
- Disruption of normal cell activities
- Heart Disease
- Damage DNA
Antioxidants
Antioxidants, such as resveratrol, can help to neutralize free radicals by donating an electron, which stabilizes the molecule and stops the chain reaction. By doing so, they can help to prevent or reduce oxidative damage in the body. This is why consuming antioxidant-rich foods or supplements, such as resveratrol, may offer health benefits.
ORAC stands for Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity
ORAC stands for Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity, which is a measure of the antioxidant capacity of a substance or food. It was developed by scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as a way to measure the ability of antioxidants to neutralize free radicals in a test tube.
The ORAC value of a substance is determined by measuring its ability to neutralize free radicals in a test tube in comparison to a standard reference antioxidant, such as Trolox. The higher the ORAC value, the more effective the substance is at neutralizing free radicals.
Is Resveratrol an Antioxidant
Yes, resveratrol is an antioxidant. It is a natural compound found in some plants, including grapes, berries, and peanuts, and is known for its potential health benefits. Resveratrol has been shown to have antioxidant properties, which means it can help to protect cells in the body from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. This may contribute to its potential health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and potentially reducing the risk of certain cancers.
It is important to note that ORAC values were determined using in vitro tests, and the results may not directly translate to the human body’s antioxidant response. Additionally, the use of ORAC values as a measure of a food or substance’s overall health benefits has been criticized as it doesn’t take into account the complex interactions between different compounds in the body and the way they may contribute to health.
Nonetheless, ORAC values can be a useful tool for comparing the antioxidant capacity of different substances or foods in vitro.
How is resveratrol different to other antioxidants
Resveratrol is different from many other antioxidants in a few ways:
- Mechanism of action: Resveratrol has been found to activate a specific group of enzymes known as sirtuins, which play a role in regulating cellular processes such as metabolism and DNA repair. This mechanism of action is different from many other antioxidants, which primarily act by neutralizing free radicals.
- Bioavailability: Resveratrol is relatively poorly absorbed by the body when consumed orally, meaning that only a small fraction of the ingested dose actually makes it into the bloodstream. This can limit its potential health benefits compared to other antioxidants that are more easily absorbed.
- Food sources: Resveratrol is found primarily in the skins of grapes and other berries, as well as in peanuts. Other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, are found in a wider variety of foods and are often consumed in larger amounts in the typical diet.
Despite these differences, resveratrol has been found to have potential health benefits similar to those of other antioxidants, such as reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and potentially reducing the risk of certain cancers.
Powerful Antioxidants – Ingredients
Blueberry juice concentrate -These health benefits have been attributed to the important number of bioactive compounds in blueberries with activities such as antioxidant, antitumor, antimutagenic, and antidiabetic effects and the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Reference: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34716717/. Blueberry juice: Bioactive compounds, health impact, and concentration technologies-A review
Pomegranate juice concentrate – Possible benefits of pomegranate juice include being an antioxidant, which may help prevent cancer and other conditions, providing vitamin C, boosting digestive health, and reducing insulin resistance. It may help with cancer prevention, immune support, and fertility. The National Institutes of Health (NIH). list pomegranate as one of the natural remedies that may help treat or prevent prostate cancer. An older, 2014 research article notes that the polyphenols in pomegranate may aid in preventing the growth of cancer cells related to prostate cancer. Reference: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318385#benefits-of-pomegranate
Sour cherry juice concentrate– Inflammation and oxidative stress are important factors in the development of cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. The findings of our previous study suggest that 12 weeks consumption of tart cherry juice lowers the levels of systolic blood pressure (BP) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in older adults. Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6413159/
In 2010, researchers at Northumbria University made a ground-breaking discovery: Montmorency tart cherry juice – already known for its high levels of phytochemicals – helped marathon runners to recover their muscle function after intense exercise. This seminal work has led to successive studies unveiling the fruit’s many remarkable health properties within and beyond the sporting arena. Reference: https://www.northumbria.ac.uk/research/research-impact-at-northumbria/economic-impact/studies-on-cherry-juice-unravel-a-multitude-of-health-benefits/
Cranberry juice concentrate – dietary components and in particular, (poly)phenol-rich fruits such as berries have been increasingly recognised for their protection against age-related neurodegeneration.. Cranberry supplementation for 12 weeks was associated with improvements in visual episodic memory in aged participants when compared to placebo. Mechanisms of action may include increased regional perfusion in the right entorhinal cortex, the accumbens area and the caudate in the cranberry group. Significant decrease in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol during the course of the intervention was also observed. Reference: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.849902/full
Japanese Sophora flowers -Quercetin supplements are made from the flower bud of Sophora japonica, the Japanese pagoda tree. Quercetin extracted from Sophora japonica flower improves growth performance, nutrient digestibility, cecal microbiota, organ indexes, and breast quality in broiler chicks. Reference:
Quercetin is Anti-inflammatory, Anti-allergenic, Anti-cancerous, Cardiac protection and the fight against hypertension. Reference: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5214562/
Rosemary leaf extract -Significant antioxidant benefits thanks to the activity of Carnosic Acid, Carnosol and Rosmarinic acid. Antioxidants can help with product and skin protection. Carnosol and carnosic acid are diterpenes, which contribute to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of rosemary extracts [41, 42]. In rosemary plants, carnosic acid protects chloroplasts from oxidative stress by scavenging free radicals [43]. Reference: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/rosmarinus-officinalis-extract
Green tea leaf extract – Polyphenol antioxidants called catechins make up the majority of green tea extract’s antioxidant content. Among the catechins in green tea, epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the most researched and thought to provide the most health benefits. Studies have shown that green tea extract increases your body’s antioxidant capacity (the activity of your body’s own antioxidant enzymes) and protects against oxidative stress. This, in turn, may prevent associated health concerns (3 4, 5 6). Reference: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/10-benefits-of-green-tea-extract#1.-High-in-antioxidants
Bitter Orange (fruit) Extract (Advantra Z®) -This self-affirmed GRAS ingredient is a standardized Citrus aurantium extract. Our C. aurantium bitter orange fruit extract is backed by multiple human efficacy clinical studies and a comprehensive safety dossier. Advantra Z® extract delivers powerful thermogenic benefits without undesirable effects. The increase in metabolism can be noted by an increase in basal metabolic rate (BMR) as well as through increased lipolysis which is the release of fatty acids into the bloodstream when the body breaks down fats and lipids.
Green coffee extract. Some research also suggests that green coffee bean extract could have health benefits, such as improving blood pressure and cholesterol levels. This belief stems from the antioxidant properties and other pharmacologically active compounds in the unroasted beans.
Green coffee extract contains chlorogenic acids. Which are a group of antioxidant compounds that scientists believe may be responsible for its health effects. Reference: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318611#_noHeaderPrefixedContent
Plum juice concentrate. The polyphenols found in prunes appear to have potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. In test tube studies markers of inflammation and oxidation dropped by 43% and 32% when prune polyphenols were used. Researchers are continuing to study the benefits of prune polyphenols in humans. Reference: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25921826/
Grape skin extract – The grape seed extract (GSE) and its main active polyphenol, resveratrol (RES), have shown considerable antioxidant activities, besides possessed protective and therapeutic effects against various skin complications. Reference: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31115657/#:~:text=The%20grape%20seed%20extract%20(GSE,effects%20against%20various%20skin%20complications
The key difference between resveratrol and grape seed extract is that resveratrol comes from grape skins, whereas grape seed extract comes from seeds of grapes. According to medical research, a combination of resveratrol and grape seed extract is very effective in killing colon cancer cells. Therefore, it is important to find their sources, properties, and other uses
Collection of Research Studies on Resveratrol and Antioxidants
Boosting immune system against cancer by resveratrol – Article link
The article discusses how boosting the immune system’s function against cancer can increase the effectiveness of anticancer therapy, as immunosuppressive responses can attenuate antitumor immunity. Resveratrol, a natural agent, has been shown to modulate the immune system to potentiate antitumor immunity by inducing the release of anticancer cytokines and inhibiting the release of immunosuppressive cytokines. Resveratrol can also sensitize cancer cells to the signals released by anticancer immune cells and stimulate the polarization of CD4+ T cells and macrophages towards anticancer cells. The article explains how resveratrol can boost the immune system against cancer by modulating immune cell responses within the tumor
Resveratrol against Cervical Cancer: Evidence from In
Vitro and In Vivo Studies – Article link
This review manuscript summarizes in vitro and animal studies that demonstrate the potential therapeutic effects of resveratrol (RSV) on cervical cancer. The studies showed that treatment with RSV reduced cell viability and proliferation, induced apoptosis and autophagy, and inhibited various signaling pathways associated with cervical cancer. Animal studies showed a decrease in tumor volume and weight. Some RSV analogs also showed higher anticancer effects. Future studies are needed to fully understand the cellular mechanisms involved and the potential of RSV as a treatment for cervical cancer in patients.
Therapeutic potential of resveratrol against emerging
respiratory viral infections – Article link
Resveratrol, a natural compound, has shown therapeutic potential in respiratory viral infections. It has been found to have anti-viral activity against various viruses such as influenza, RSV, HCoV, HRV and hMPV. Resveratrol can inhibit viral replication and modulate the host immune response. The compound’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties could also alleviate symptoms associated with respiratory virus-related diseases.
Mechanisms of AGING and the Preventative Effects of
Resveratrol on Age-Related Disease- Article Link
Summary: Aging is a natural process that can lead to various diseases. Eating a healthy diet can help prevent these diseases and possibly increase lifespan. Resveratrol, a phytochemical found in plants, has been shown to slow down aging and improve health in several model organisms. Resveratrol can regulate various cellular functions such as mitochondrial function, cancer cell growth, and inflammation. Some human studies have suggested that resveratrol can help prevent diabetes, heart disease, and neurological diseases. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness and safety. The main challenge in using resveratrol as a drug is its low bioavailability and non-specific activity. Therefore, more studies are needed to find the best dose and effective delivery system for long-term use. Despite these challenges, resveratrol can be an important functional food and food supplement to prevent age-related diseases.
The Cytotoxicity Effect of Resveratrol; Cell Cycle
Arrest and Induced Apoptosis of Breast Cancer – Article link
The study found that resveratrol, a compound found in red wine and other foods, can cause cell death in breast cancer cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The researchers used transcriptome profiles to identify genes that were affected by resveratrol and found that they were mostly related to cell death and the cell cycle. The study also found that the cells were arrested in a particular phase of the cell cycle. The study suggests that resveratrol may have potential as a treatment for breast cancer, but further research is needed.
Evidence for anti inflammatory and antioxidative properties of dried plum polyphenols in marcrophange – Article link
The study tested how well dried plum polyphenols can fight inflammation and damage in cells. They found that these polyphenols can reduce the harmful effects of substances that can damage cells by 32%. This suggests that dried plum polyphenols have potential health benefits, but more research is needed to confirm these findings in people.
Effects of Tart Cherry Juice on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Older Adults – Article link
Regular consumption of tart cherry juice may help to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults by reducing systolic blood pressure and LDL cholesterol. This effect is possibly due to the juice’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, as shown by increased DNA repair activity and reduced CRP levels. The study emphasizes the benefits of consuming fruits and vegetables for a healthy heart and suggests further investigation in larger and longer-term trials involving older adults.
Chronic Consumption of Cranberries for 12 weeks improves Episodic Memory and Regional Brain Perfusion in Healthy Older Adults: A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Groups Feasibility Study – Article link
Results: Cranberry supplementation for 12 weeks was associated with improvements in visual episodic memory in aged participants when compared to placebo. Mechanisms of action may include increased regional perfusion in the right entorhinal cortex, the accumbens area and the caudate in the cranberry group. Significant decrease in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol during the course of the intervention was also observed. No significant differences were, however, detected for BDNF levels between groups.
Conclusions: The results of this study indicate that daily cranberry supplementation (equivalent to 1 small cup of cranberries) over a 12-week period improves episodic memory performance and neural functioning, providing a basis for future investigations to determine efficacy in the context of neurological disease. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT03679533 and at ISRCTN as ISRCTN76069316.
Studies on cherry juice unravel a multitude of health benefit- Article link
The research suggests that drinking tart cherry juice regularly can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults by lowering their systolic blood pressure and LDL cholesterol. This effect may be due to the juice’s anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties. The study reinforces the importance of consuming fruits and vegetables to improve heart health. The researchers recommend further investigation in larger and longer-term trials involving older adults.
Plum juice but not dried plum powder is effective – Article link
The study found that rats who drank plum juice had improved working memory in the Morris water maze compared to those fed dried plum powder or the control group. The difference may be due to the larger amount of phenolics consumed in the juice group. The study concludes that the amount and type of phenolics in the plum products should be considered in relation to cognitive benefits reported in other dietary intervention studies.
Quercetin extracted from Sophora japonica flower improves growth performance, nutrient digestibility, cecal microbiota, organ indexes, and breast quality in broiler chick – Article link
The study found that increasing the dosage of QS in the diet of broiler chicks had positive effects on body weight gain, feed intake, dry matter digestibility, energy retention, cecal bacteria counts, breast muscle yield, pH value, water holding capacity, and drip loss. Overall, the addition of QS improved the growth performance of broiler chicks and their breast muscle quality.
How to get more antioxidants in your diet
- Eat more fruits and vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are great sources of antioxidants, so try to eat a variety of colorful produce every day. 2 Fruit 5 Vegetable Servings a day.
- Drink tea: Tea, especially green tea, is rich in antioxidants called catechins. Drinking tea regularly can help boost your antioxidant intake.
- Include whole grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats contain antioxidants like ferulic acid and phytic acid.
- Add herbs and spices: Many herbs and spices like turmeric, cinnamon, and oregano are high in antioxidants and can be easily added to your meals.
- Snack on nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds like almonds, walnuts, and sunflower seeds contain antioxidants like vitamin E and selenium.
- Consider supplements: While it’s best to get your antioxidants from whole foods, supplements can be helpful if you’re not getting enough from your diet alone.
By incorporating more antioxidant-rich foods into your diet, you can help protect your body from the damaging effects of free radicals and promote better health.
The best type of Resveratrol Antioxidant Drink
- Purchase from a reputable manufacturer that does NOT fairy dust.
- Look for a cGMP Manufacturer. cGMP is a set of regulations and guidelines established by regulatory agencies to ensure that pharmaceutical, biotech, and medical device products are consistently manufactured to meet quality and safety standards.
- Purchase a product that uses nanotechnology to make each ½- ¾ ounce serving 250 times more available than encapsulated Resveratrol.
- When exposed to air it is quickly destroyed. You want a product that is preserved by modifying the atmosphere of the liquid in the bottle with nitrogen. Oxygen is pushed out of the bottle before sealing it this vastly reduces the chances of the ingredients (antioxidants including resveratrol) oxidizing (e.g. being destroyed). (reference)
- Look for a Resveratrol product that has additional antioxidants such as those mentioned.
Katie Larking, Nutrition and Health Coach is on a mission to help people (and their pets) wake up feeling healthier and happier. She is committed to inform, educate and empower others to make healthy choices, through diet and lifestyle changes. Katie has competed in two Fitness Competitions for the Australian Natural Body Building over 40s division, placing 2nd and 3rd. Katie has studied nutrition, weight management, and fat loss. Katie has a Bachelor of Applied Science in Health Promotion (BAppSc) and an Advanced Certificate in Nutrition and Health for Anxiety, Depression and Stress. She is a qualified Nutrition and Health Coach and is a member of the International Institute for Complementary Therapists. Katie takes a holistic approach to care. This means that you are supported as a whole person, incorporating physical, emotional and spiritual needs. Her main interests include preventative health, nutrition, age reversal science, and weight lifting. Connect with her today using the links below; she would love to hear from you.